Visit the MAPLES project website, University of Oslo
MAgma PLays with sEdimentary rockS (MAPLES) is a research project lead by Dr. Sara Callegaro, at Department of Geosciences, and the research centre CEED, both University of Oslo, Norway.
The MAPLES project is a Young Talent project sponsored by the Norwegian Research Council (NFR), and the aim to investigating interactions between intrusive magma bodies and their sedimentary host rocks.
The SEM is a powerful tool in this endeavor, allowing to image sill-host rock contacts at high magnification, sometimes even in 3D with secondary electrons, and to produce element maps of areas of interest by EDS. The three examples here show sills from the Siberian Traps large igneous province, intruded in evaporitic host-rocks.
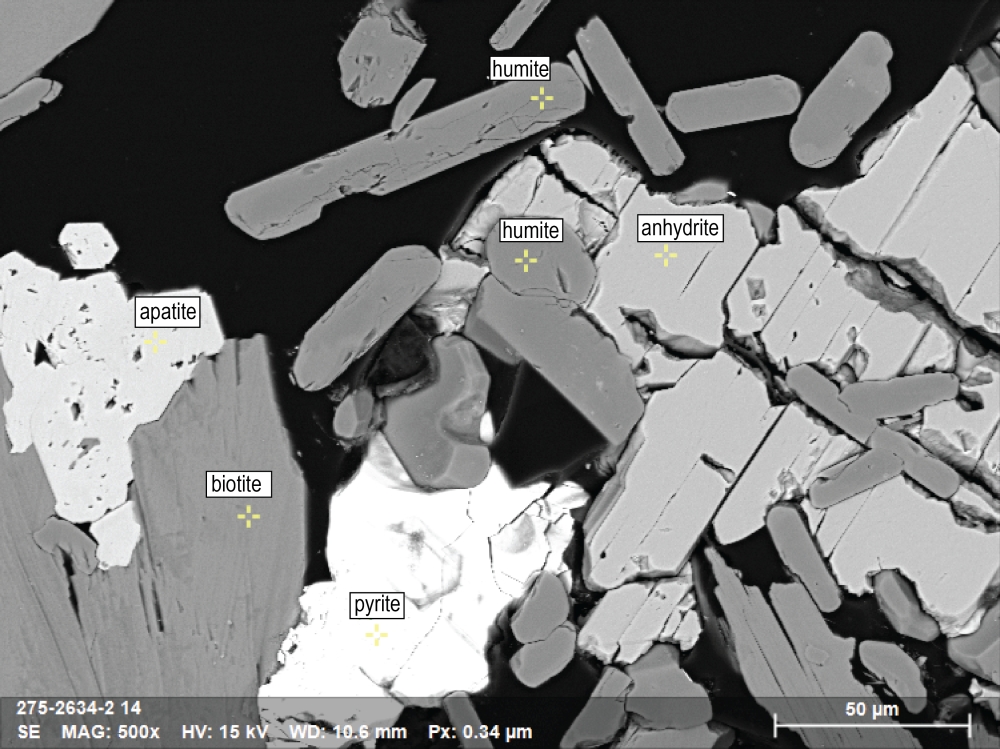
In this BSE image (image A), thermal metamorphism affects an anhydrite-rich dolostone host rock, with the formation of humite at the expenses of anhydrite. Biotite, apatite and sulfides are also produced. The phases were identified using the EDS.
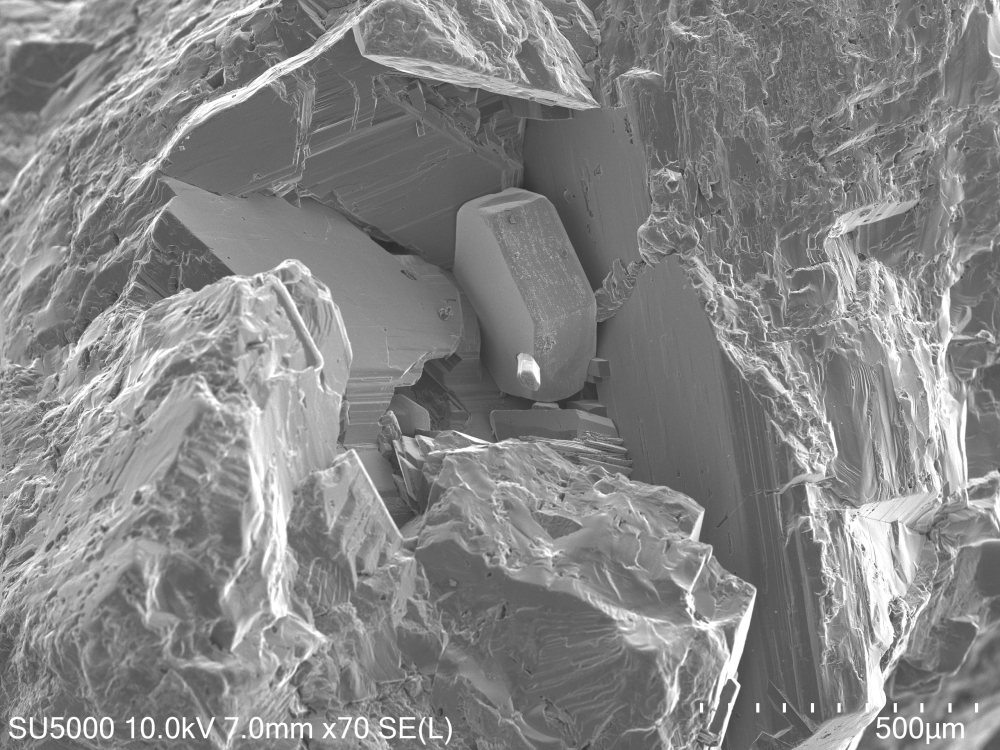

Secondary Electrons give a strong 3D effect (image B) to this miarolitic cavity isolated in a framework of large plagioclase crystals. A sulfide is visible in the cavity, with a small apatite crystal sticking out.
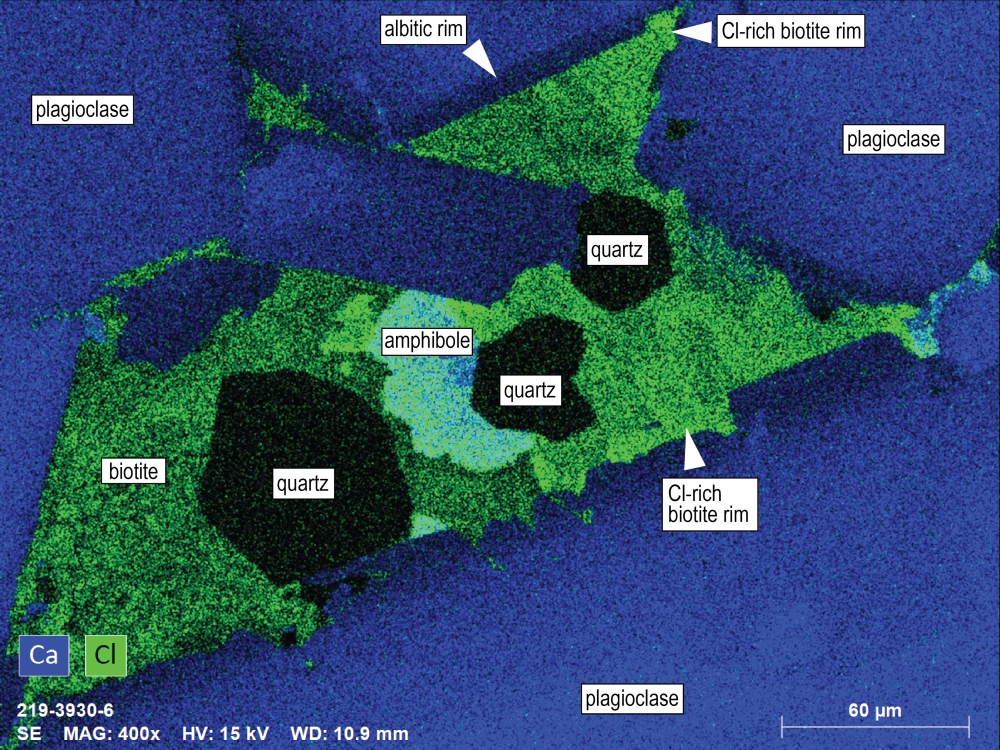
An element map (Cl and Ca; Image C) of a late-stage evolved interstitial pocket is obtained with EDS. We can distinguish between Cl-rich biotite (particularly Cl-rich at the rims) and Cl-rich amphibole. Plagioclase crystals enclosing the pocket show clear albitic rims, in a late-stage sill system dominated by Na and Cl mobilized from the evaporitic (halite-rich) host rocks.
Additional information
- The MAPLES project started in 2020 and with an end in 2024.
- About the research (URL): www.mn.uio.no/geo/english/research/projects/maples/