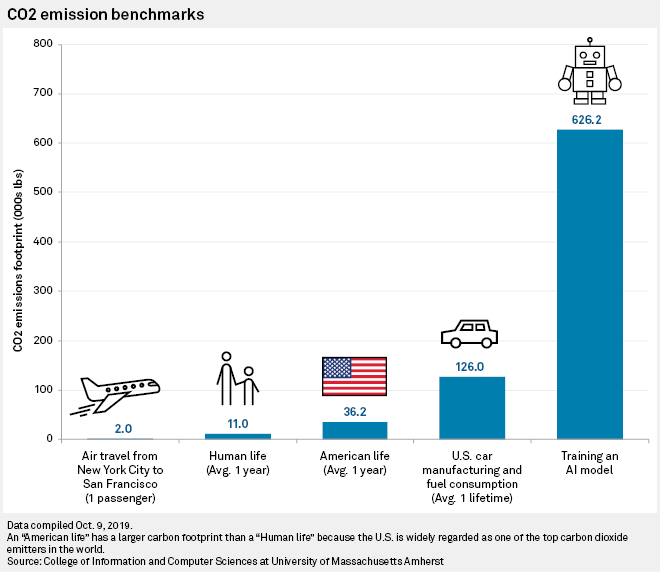
Artificially intelligent services are penetrating our everyday life. Digital assistants, home automation and route planning are just a few examples of how our lives have become intertwined with the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning. We have heard of AI models with billions of parameters to tune in training and some efforts have gone into assessing the carbon footprint of such approaches. However, what is unknown as of yet, is the carbon footprint of the devices at the edge of the network that perform the inference and / or communicate with the backend data centers for inference. While it seems that any one of these devices in and onto itself does not contribute much to the carbon footprint, it is the mass-adoption, the pervasive presence of these devices everywhere that may constitute a multiplier in accelerating the carbon output without anyone realizing.
This thesis will look at the edge of the network and determine the carbon footprint of these edge devices as they partake in AI and machine learning.
Qualification: The ideal candidate has interdisciplinary knowledge as may be acquired in curricula emphasising sustainability, energy informatics and related disciplines.