The solar wind, composed of charged particles from the Sun, varies in speed, density, and composition based on its source on the Sun’s surface. Understanding its origin has been challenging due to the dispersion of details by the time it reaches Earth.
The Role of Solar Orbiter's Instruments
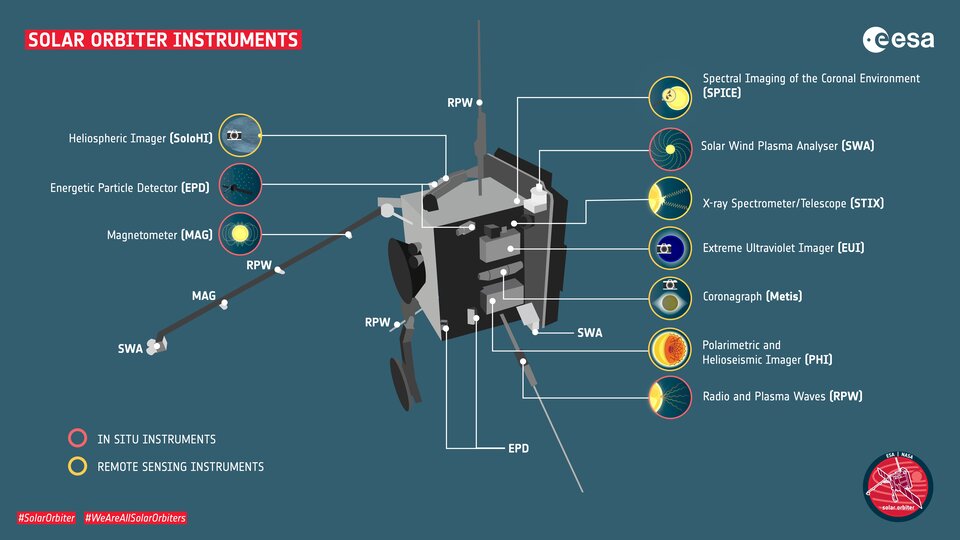
The Solar Orbiter’s unique combination of in situ instruments, which measure solar wind around the spacecraft, and remote sensing instruments, which capture images of the Sun, made this connection possible. Using the Magnetic Connectivity Tool, researchers predicted where the spacecraft would intersect the solar wind emitted from specific surface features.
Key Data Collection
Between 1 and 9 March 2022, when the Solar Orbiter was 75 million km from the Sun, it gathered crucial data, showing a link between the solar wind and its source regions, such as coronal holes and active regions with sunspots.
Future Implications
This success confirms that Solar Orbiter can robustly connect the solar wind to its source on the Sun, fulfilling a primary mission objective and paving the way for more detailed studies of the solar wind’s origin.
Further Reading
For further reading, see 'Multi-source connectivity as the driver of solar wind variability in the heliosphere' by Stephanie Yardley et al., published in Nature Astronomy.
